This knowledgebase article provides detailed best practices for securing your cPanel hosting account. cPanel is a popular web hosting control panel that manages websites, emails, files, databases, and more. Security is crucial to protect against threats like hacking, malware, spam, and data breaches. We’ll cover every relevant cPanel feature, including two-factor authentication (2FA), virus scans, malware protection, and others, with step-by-step instructions where applicable. These recommendations are based on official cPanel documentation and industry best practices.
We’ll address security for emails, files, databases, and the overall account. Always consult your hosting provider for server-level configurations, as some features may require admin access via WHM (WebHost Manager).
1. Understanding cPanel Security Basics
Before diving in, log in to your cPanel dashboard securely. Use a strong, unique password and access it via HTTPS (e.g., https://yourdomain.com:2083). Avoid public Wi-Fi for logins.
Here’s a screenshot of a typical cPanel dashboard for reference:

The cPanel Layout | LogicWeb
Key principles:
- Keep everything updated: Regularly update cPanel, WHM, themes, plugins, and CMS (e.g., WordPress) to patch vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords: Enforce complex passwords (at least 12 characters, mix of letters, numbers, symbols) for all accounts.
- Enable backups: Use cPanel’s Backup Wizard to schedule automatic backups of files, emails, and databases. Restore from pre-compromise states if hacked.
- Monitor activity: Check cPanel’s Metrics section (e.g., Visitors, Errors) for suspicious patterns.
Differentiate between site compromises (affecting one website) and root compromises (affecting the entire server). In case of compromise, identify entry points like insecure plugins and restore from backups.
2. Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method (e.g., app-generated code) alongside your password. It’s essential for preventing unauthorized access.
Steps to Set Up 2FA in cPanel:
- Log in to cPanel and navigate to the Security section.
- Click on Two-Factor Authentication.
- If not enabled, click Set Up Two-Factor Authentication.
- Download a 2FA app like Google Authenticator or Authy on your mobile device.
- Scan the QR code displayed in cPanel with your app.
- Enter the 6-digit code generated by the app to verify.
- Click Activate. You’ll now need this code for future logins.
For management: You can regenerate the QR code or remove 2FA if needed, but keep backup codes secure.
Here’s a screenshot of the 2FA setup interface:
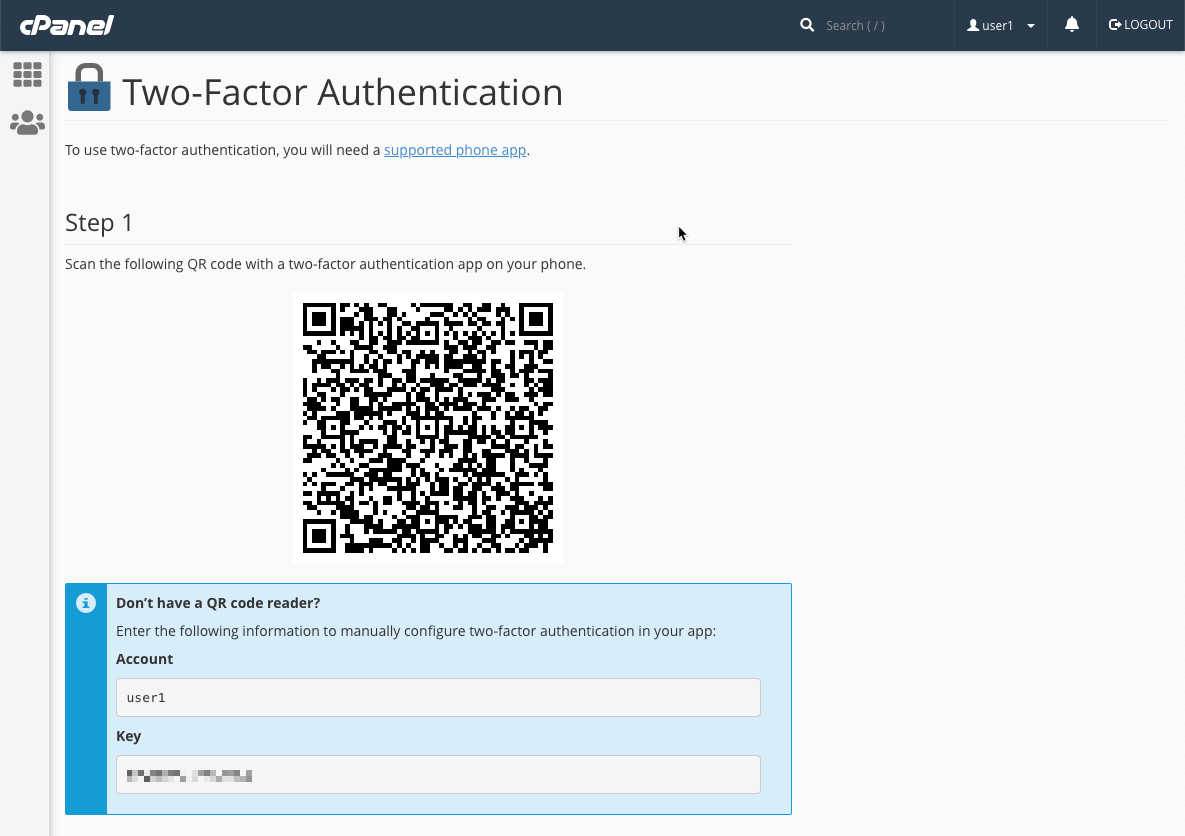
How to Configure and Use Two-Factor Authentication in cPanel | cPanel
Pro Tip: Enable 2FA for all services, including email and FTP accounts.
3. Virus Scans and Malware Protection
cPanel includes built-in tools to scan for viruses and malware. Regular scans help detect and remove threats from files, emails, and public directories.
Using the Virus Scanner:
- In cPanel, go to Security > Virus Scanner.
- Select scan options: Scan Mail (for emails), Scan Entire Home Directory (for all files), Scan Public Web Space (for website files), or Scan Public FTP Space.
- Click Scan Now.
- Review results; quarantine or delete infected files.
- Schedule regular scans via cron jobs if supported by your host.
For advanced malware protection, some hosts integrate tools like Imunify360 or ClamAV, which provide real-time scanning and automatic removal. Prevent malware by avoiding nulled/pirated themes/plugins and scanning uploads.
Here’s a screenshot of the Virus Scanner interface:
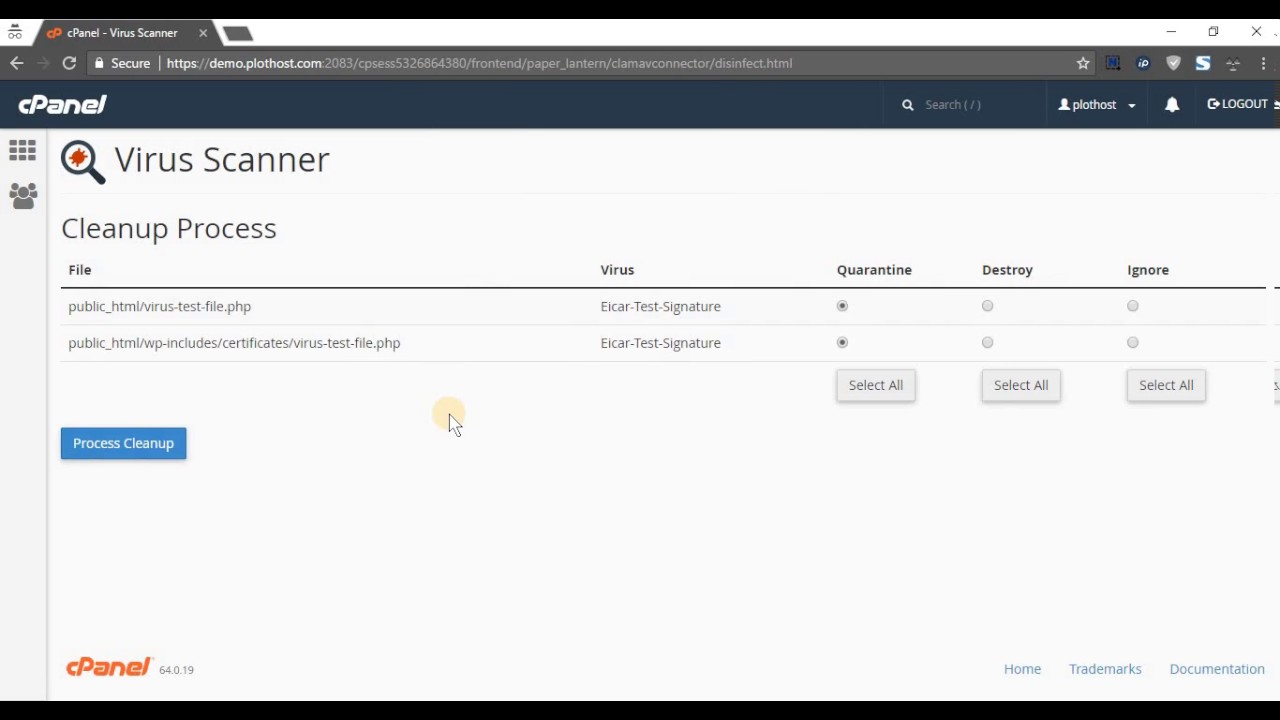
How to run a Virus Scan from cPanel – PlotHost
If no backups exist post-infection, manual cleaning requires expertise—consider hiring a professional.
4. File Security
Secure files to prevent unauthorized access, modifications, or theft.
Best Practices:
- File Permissions: Use cPanel’s File Manager to set permissions. Directories should be 755, files 644. Avoid 777 (world-writable) to prevent exploits.
- Steps: Right-click a file/folder in File Manager > Change Permissions > Adjust checkboxes > Change Permissions.
Here’s a screenshot of changing file permissions:
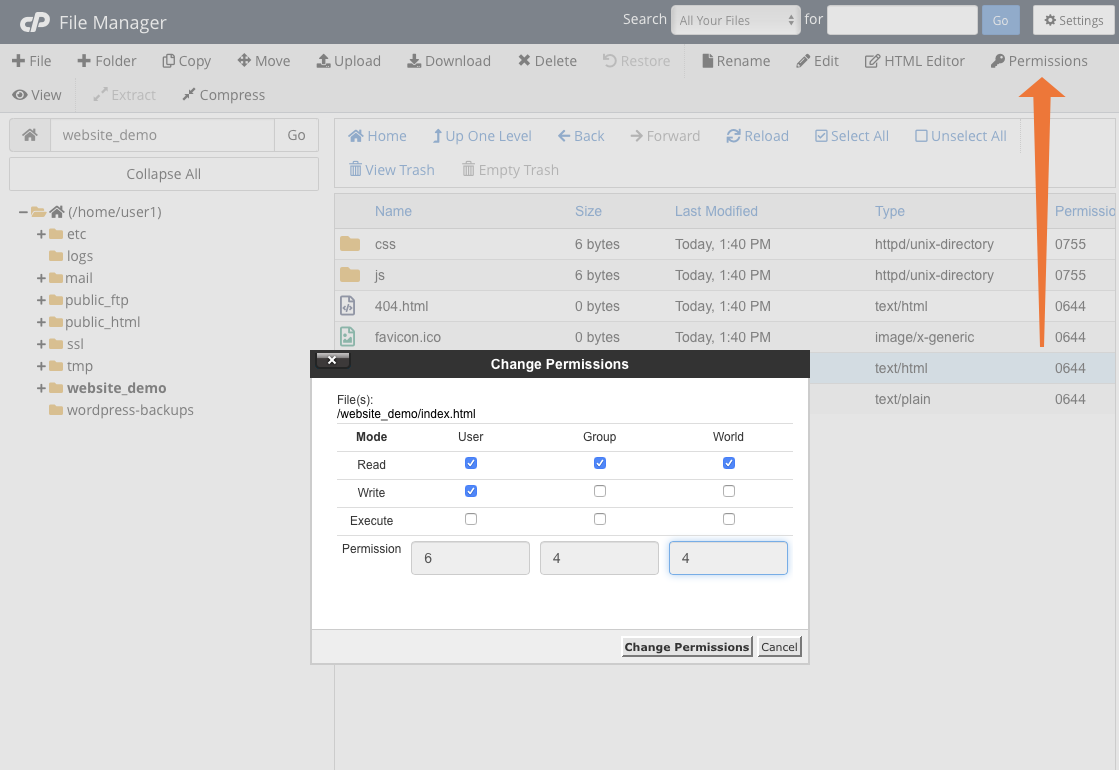
How to Assign Permissions to Files and Folders in cPanel | cPanel
- Hotlink Protection: Prevents bandwidth theft by blocking other sites from embedding your images/files.
- Steps: Go to Security > Hotlink Protection > Enable > Add allowed referrers (e.g., your domain) > Block extensions (e.g., .jpg) > Submit.
Here’s a screenshot of Hotlink Protection:
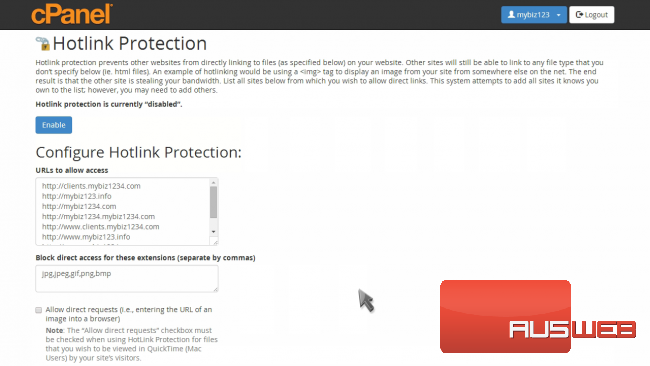
How to setup hotlink protection in cPanel – Web24
- Leech Protection: Limits login attempts to directories with passwords.
- Disable Directory Indexing: Edit .htaccess to prevent listing of directory contents.
- Scan files regularly with the Virus Scanner.
5. Email Security
Emails are common attack vectors for spam, phishing, and malware.
Best Practices:
- Spam Filters: Use Apache SpamAssassin in cPanel.
- Steps: Go to Email > Spam Filters > Enable > Configure settings (e.g., score thresholds) > Process.
Here’s a screenshot of Spam Filters:
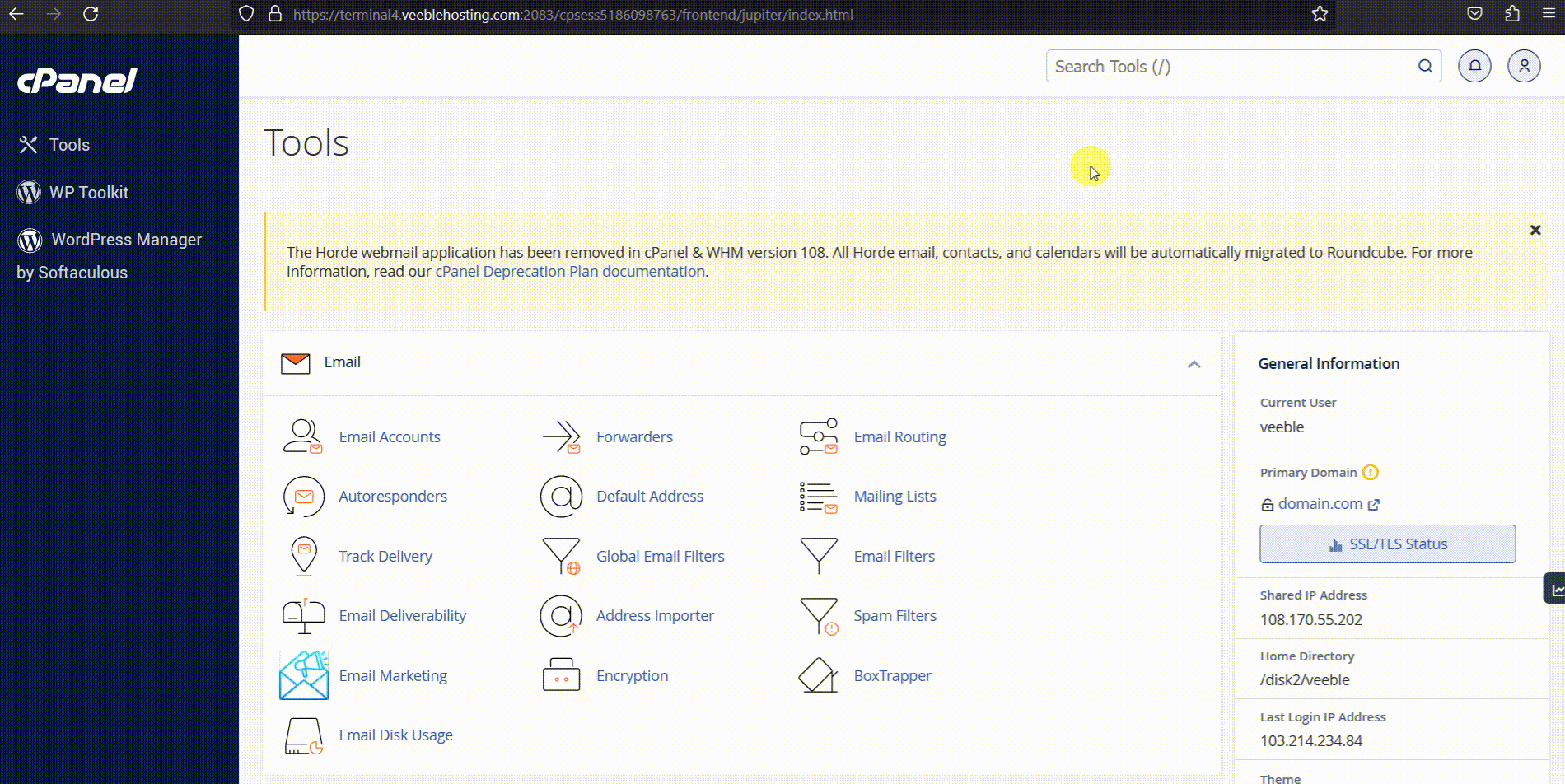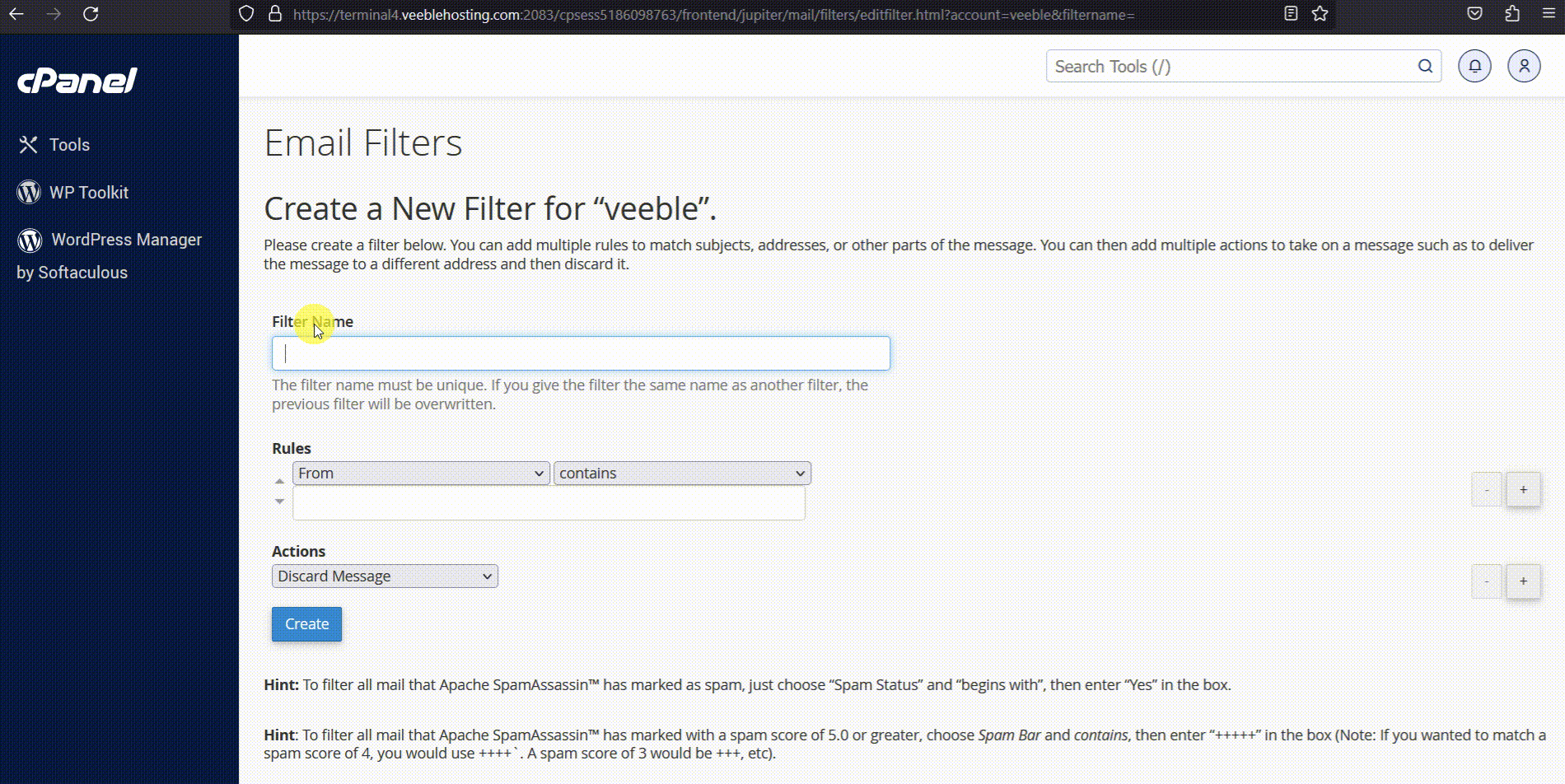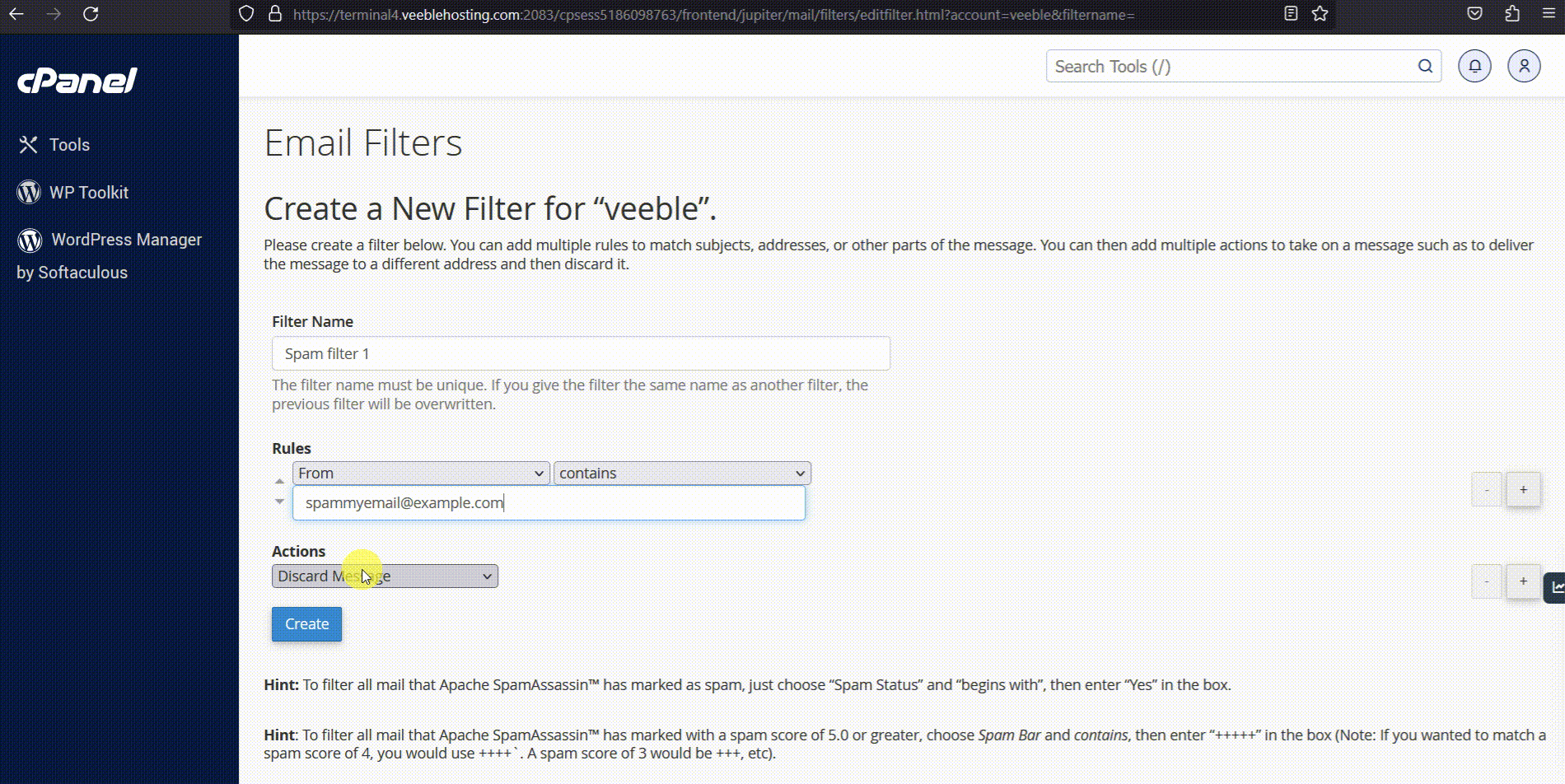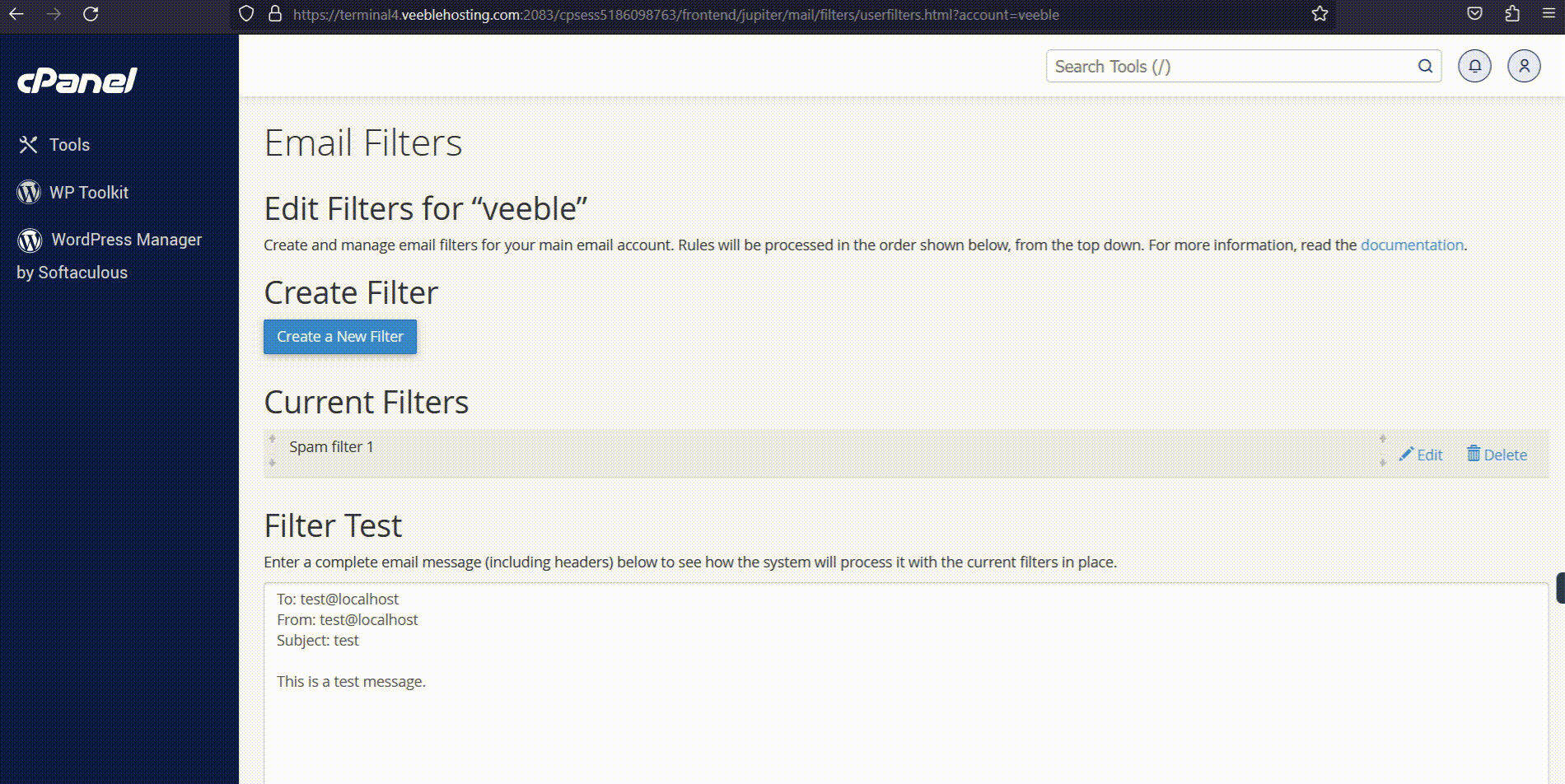
How to Configure Spam Filters in cPanel – Veeble Hosting
- Email Authentication: Enable DKIM and SPF to prevent spoofing.
- Steps: Email > Email Deliverability > Manage records.
- Secure Connections: Use SSL/TLS for email clients (IMAP/POP3/SMTP).
- BoxTrapper and Filters: Block suspicious emails or forwarders.
- Monitor for abuse: Check email queues and remove suspicious forwarders.
- Limit email sending to prevent spam blacklisting.
6. Database Security
Databases store sensitive data; secure them to avoid SQL injections and unauthorized access.
Best Practices:
- User Privileges: Grant minimal privileges.
- Steps: Go to Databases > MySQL Databases > Under Current Databases, click Privileges > Select user > Edit Privileges > Check only needed options (e.g., SELECT, INSERT) > Make Changes.
Here’s a screenshot of database privileges:
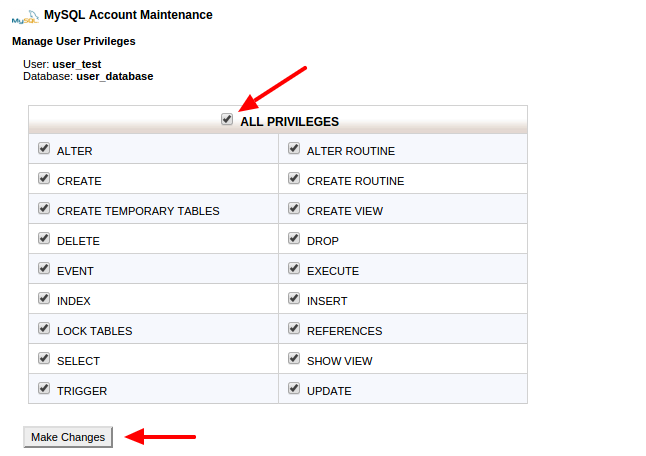
cpanel-database-user-privileges-by-codexworld – CodexWorld
- Remote MySQL: Restrict remote access to specific IPs via Databases > Remote MySQL.
- Use strong database passwords and change them regularly.
- Backup databases via phpMyAdmin or Backup Wizard.
- Avoid storing sensitive data unencrypted; use hashing for passwords.
7. Advanced Security Features
- IP Blocker: Block malicious IPs from accessing your site.
- Steps: Security > IP Blocker > Enter IP/range (e.g., 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.1.0/24) > Add. This edits .htaccess and affects website access only.
Here’s a screenshot of IP Blocker:
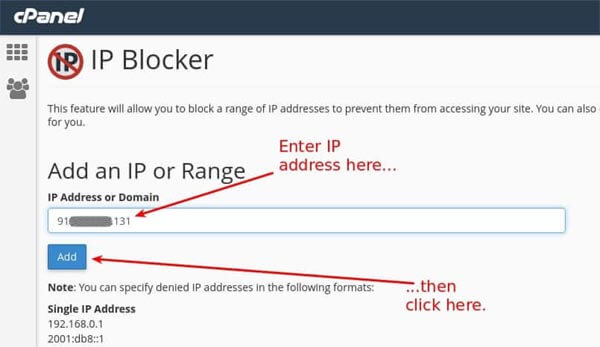
Using the IP Blocker in cPanel
- ModSecurity: Web Application Firewall (WAF) to block common attacks.
- Steps: Security > ModSecurity > Enable for all domains > Toggle per domain if needed. Requires mod_security2 module installed.
Here’s a screenshot of ModSecurity configuration:
How To Install and Configure ModSecurity™ In cPanel | cPanel
- SSL/TLS Manager: Secure data in transit.
- Steps: Security > SSL/TLS > Install/manage certificates > Enable for websites, emails. Use AutoSSL for free certificates.
Here’s a screenshot of SSL/TLS Manager:
SSL/TLS Status feature in cPanel – Interserver Tips
- cPHulk Brute Force Protection: In WHM (admin-level), but users can report issues to hosts.
- Firewall Integration: Use CSF or similar if available.
- Security Advisor: In cPanel, run Security Advisor to identify vulnerabilities.
8. Additional Tips and Monitoring
- Restrict FTP/SFTP access: Use SFTP over FTP for encryption.
- Disable unused services/features via Feature Manager (host-level).
- Use .htaccess for additional rules (e.g., block bots).
- Regularly review logs: Metrics > Raw Access or Errors.
- Educate users: If managing multiple accounts, enforce policies.
- In case of hack: Change all passwords, scan everything, restore backups, and investigate entry points (e.g., trojans, weak plugins).
By implementing these measures, you’ll significantly reduce risks. Security is ongoing—review and update regularly. If you’re unsure, contact your hosting support.

