In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, AI agents and agentic AI stand out as transformative technologies poised to redefine how we interact with machines. As we enter 2026, these systems are no longer just theoretical concepts but practical tools driving efficiency across industries. This comprehensive guide explores what AI agents and agentic AI are, their key differences, how they work, real-world examples, applications, challenges, and future trends. Whether you’re a business leader, developer, or AI enthusiast searching for “what is agentic AI” or “AI agents examples,” this article provides in-depth insights to help you navigate this exciting frontier.
What is Agentic AI?
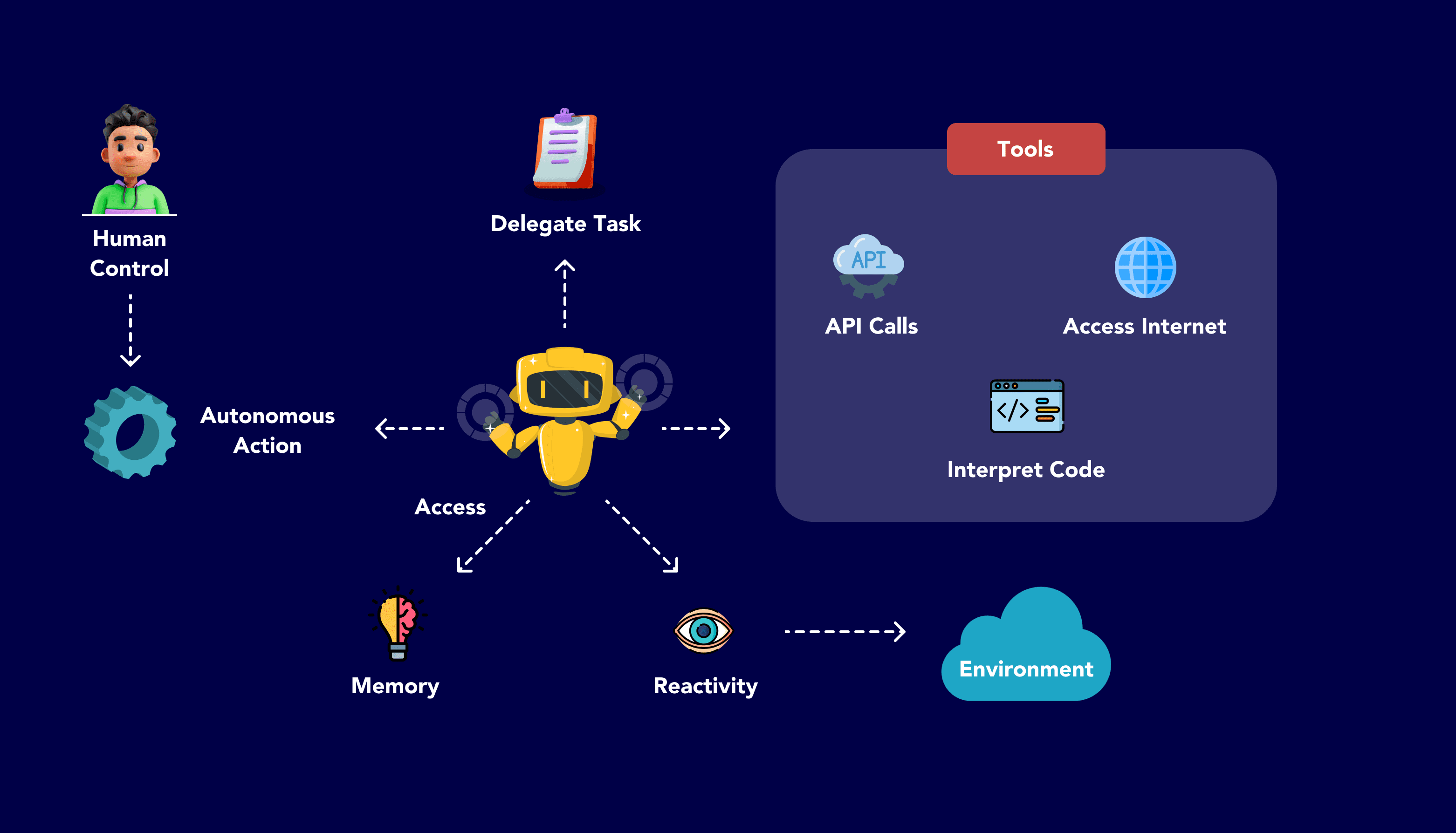
Agentic AI refers to advanced artificial intelligence systems that exhibit agency—meaning they can autonomously perceive their environment, reason over complex goals, plan multi-step actions, and execute tasks with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional AI, which relies on predefined rules or direct prompts, agentic AI adapts dynamically to new information and contexts, making it ideal for unpredictable real-world scenarios.
At its core, agentic AI builds on large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or beyond, but it goes further by incorporating reasoning engines, memory systems, and tool integrations. For instance, it can break down a high-level goal, such as “optimize a supply chain,” into subtasks like data analysis, forecasting, and decision-making. This autonomy is what sets agentic AI apart, enabling it to function as a “digital co-worker” in enterprises.
AI Agent Examples: Transforming Technology – Codoid
Key Differences Between AI Agents and Agentic AI
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there’s a nuanced distinction. AI agents are software entities designed for specific, narrow tasks within a defined domain. They perceive inputs, process them, and act accordingly—think of a simple chatbot handling customer queries or a recommendation engine suggesting products.
Agentic AI, on the other hand, represents a more sophisticated evolution. It coordinates multiple agents, manages dependencies across systems, and pursues broader objectives. For example, an AI agent might retrieve data from a database, but agentic AI could orchestrate a team of agents to analyze market trends, predict disruptions, and adjust strategies in real-time. According to industry experts, by 2026, 40% of enterprise applications will incorporate task-specific AI agents, up from less than 5% in 2025.
Here’s a quick comparison table for clarity:
| Aspect | AI Agents | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Narrow, task-specific | Broad, goal-oriented |
| Autonomy | Limited to predefined actions | High, with adaptive planning |
| Complexity | Single-domain | Multi-agent coordination |
| Examples | Chatbots, virtual assistants | Autonomous supply chain optimizers |
| 2026 Adoption | Widespread in apps | Emerging in enterprise workflows |
This distinction is crucial for businesses implementing AI solutions, as agentic systems offer greater scalability for complex operations.
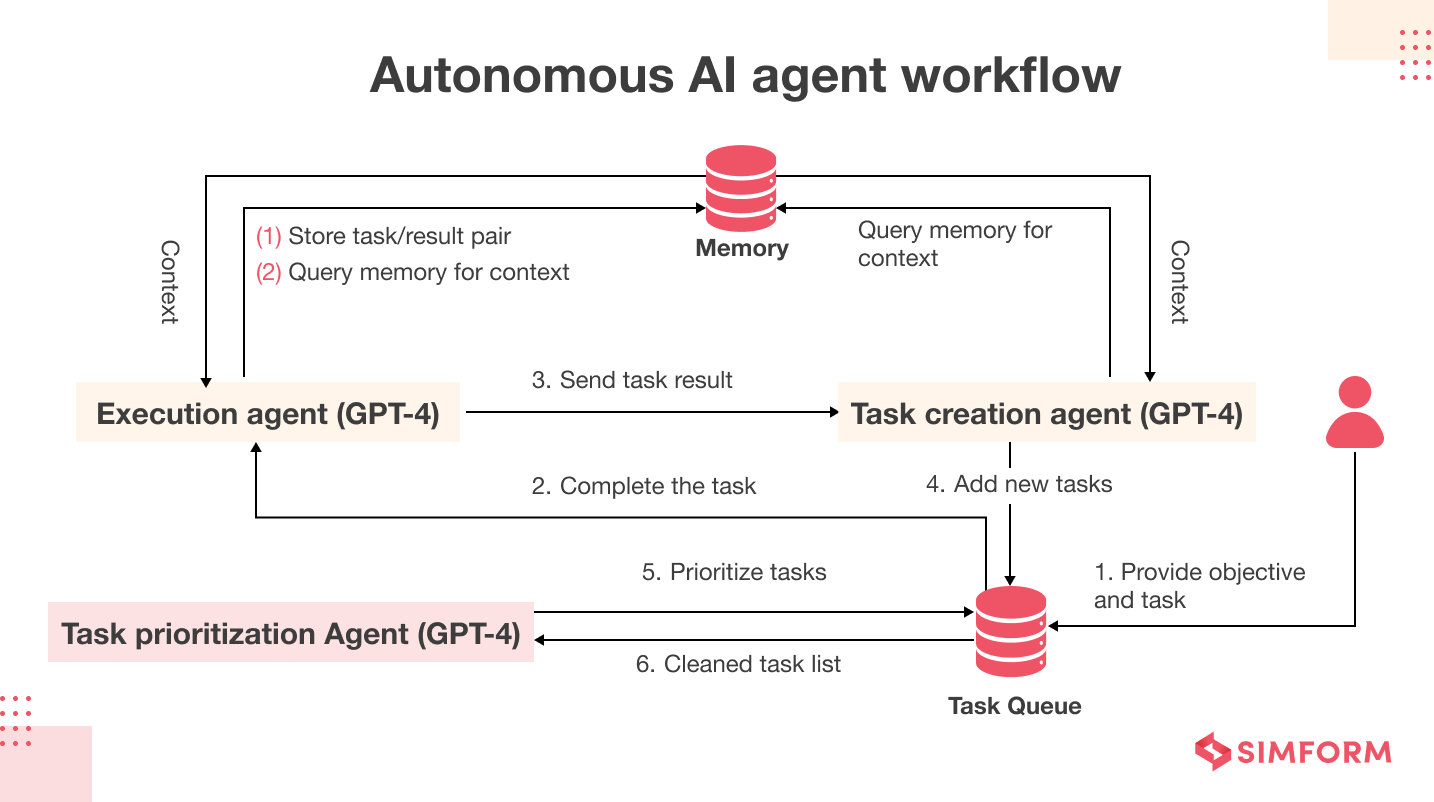
How Agentic AI Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Agentic AI operates through a structured yet flexible process, often powered by LLMs as the central reasoning engine. Here’s how it typically functions:
- Perception: The system gathers data from sensors, databases, APIs, or user inputs. This could include real-time environmental data or historical records.
- Reasoning and Planning: Using techniques like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), the AI analyzes context, breaks down goals into subtasks, and prioritizes actions. For example, it might query a knowledge graph for relevant information.
- Coordination: In multi-agent setups, it delegates tasks to specialized agents—e.g., one for data analysis, another for execution.
- Action and Adaptation: The AI executes plans via tools (e.g., APIs, robotics) and iterates based on feedback, learning from outcomes.
- Memory: Long-term memory stores past interactions for future reference, enabling continuous improvement.
This workflow allows agentic AI to handle dynamic tasks, such as fraud detection or personalized healthcare plans. Tools like NVIDIA’s agentic frameworks emphasize iterative planning for complex problem-solving.
What is an AI Agent? Characteristics, Advantages, Challenges …
For a visual representation of multi-agent systems, consider this diagram illustrating coordination in agentic architectures.
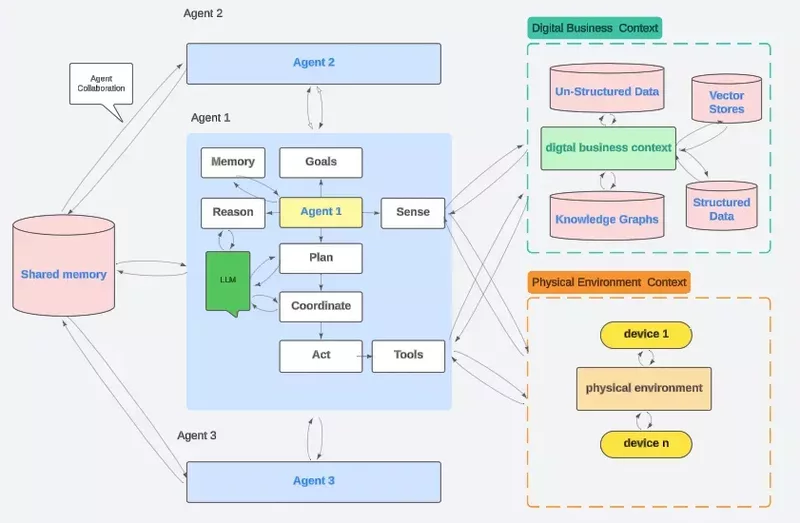
The Anatomy of Agentic AI | International Institute for Analytics
Types of AI Agents
AI agents come in various forms, each suited to different levels of complexity:
- Simple Reflex Agents: React to immediate inputs without memory, like a thermostat adjusting temperature.
- Model-Based Agents: Maintain an internal model of the world for better decision-making, e.g., navigation systems in autonomous vehicles.
- Goal-Based Agents: Pursue specific objectives, such as a search engine optimizing results.
- Utility-Based Agents: Evaluate actions based on desirability, ideal for resource allocation.
- Learning Agents: Adapt over time through machine learning, common in recommendation systems.
- Multi-Agent Systems: Collaborate like a team, central to agentic AI.
In 2026, multi-agent systems are gaining traction for enterprise use, as seen in platforms like IBM’s AI agents for customer service and procurement.
Real-World Examples and Applications of AI Agents and Agentic AI
Agentic AI is already making waves across sectors. Here are numerous examples, drawing heavily from the AI tool discovery platform at LogicWeb Discover, which catalogs over 11,888 AI tools. While not all are explicitly agentic, many exhibit autonomous behaviors akin to agents. We’ll integrate these with broader industry cases for a comprehensive view.
Examples from LogicWeb’s AI Discover Hub
LogicWeb’s directory highlights tools that act as semi-autonomous agents:
- µScale: An image upscaling tool that autonomously enhances visuals without user micromanagement. It perceives low-res inputs, reasons on pixel data, and executes high-quality outputs—perfect for creative workflows.
- Zzzcode: AI-assisted coding agent that generates, reviews, and optimizes code. It can invoke skills like best practices checks, as noted in recent X discussions on explicit tool invocation for predictability.
- Zyro: A no-code website builder that acts as an agentic system by automating design, layout, and content suggestions based on user goals.
- Zoom AI Companion: Analyzes meetings in real-time, summarizing discussions and suggesting actions—embodying agentic coordination for productivity.
Beyond these, LogicWeb features agent-like tools for tasks like content generation and data processing, showcasing the breadth of autonomous AI applications.
Broader Industry Examples
Expanding on LogicWeb’s inspirations, here are 20+ real-world agentic AI examples from 2026:
- Healthcare: Agentic systems screen medical images for anomalies, assist in diagnostics, and create personalized treatment plans. For instance, AI agents in hospitals analyze patient data to predict diseases.
- Finance: Autonomous trading agents analyze market data and execute trades. Tools like those on LogicWeb for financial AI mirror this, with utility-based agents optimizing portfolios.
- Customer Service: Concierge agents handle inquiries, schedule tasks, and resolve issues proactively. Dialpad’s agentic AI examples include e-commerce assistants providing real-time recommendations.
- Supply Chain: Multi-agent systems optimize logistics, predicting disruptions and rerouting shipments. BCG highlights AI agents automating data analysis and decision-making.
- Cybersecurity: Agents monitor networks for threats, adapting defenses in real-time. Exabeam’s use cases show agentic AI identifying patterns beyond human speed.
- Human Resources: AI agents streamline recruitment by screening resumes and scheduling interviews autonomously.
- Sales and Marketing: Agents personalize campaigns, with tools like Aisera’s examples automating lead generation.
- Robotics: Physical agents perform manufacturing tasks, lifting objects, or navigating environments.
- Gaming: Non-player characters adapt to player behavior using learning agents.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Goal-based agents make navigation decisions, avoiding obstacles.
Additional examples from X include AI agents for coding (e.g., invoking skills explicitly) and multi-agent coordination shifting AI from tools to systems.
For visual context, here’s an infographic of real-world AI agent applications:

The Future of AI Agents: Autonomous Decision-Making with AI – K21 …
Tools and Platforms for Building Agentic AI
Popular frameworks include:
- CrewAI: For multi-agent collaboration.
- LangGraph: Builds agentic workflows.
- IBM Watson: Enterprise-grade AI agents.
- Moveworks: Specializes in enterprise agentic systems.
LogicWeb AI Discover Hub is an excellent resource for exploring these and more: Visit LogicWeb Discover.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite promise, challenges include data privacy, bias in decision-making, and job displacement. Ethical AI design is key, with calls for transparency and human oversight. In 2026, regulations are evolving to address these.
Future Trends in Agentic AI for 2026 and Beyond
By 2027, agentic AI will integrate deeper into daily life, with trends like on-device agents for privacy and AI as co-workers. Predictions include new pricing models (e.g., per-task fees) and broader adoption in unpredictable operations. Conceptual art envisions a world where agents handle everything from smart cities to personalized education.

Agentic AI: The new frontier in AI evolution | Deloitte Luxembourg …
Conclusion
AI agents and agentic AI are revolutionizing autonomy in technology, offering unprecedented efficiency and innovation. From LogicWeb’s tool examples to enterprise applications, the potential is vast. As we advance into 2026, embracing these systems with ethical foresight will unlock their full value. For more on AI trends, check resources like IBM’s AI Agents Guide or explore NVIDIA’s Blog. Stay ahead by experimenting with agentic tools today.




